As an experienced dental surgeon, you often face mouth sores, tooth discoloration, and gum pain complaints from patients. These issues mostly arise due to using traditional orthodontics, such as metal braces. Brackets and wires rub the cheeks and lips. This causes cuts and discomfort. Patients also struggle to keep their teeth clean.
It stresses both you and your patients. However, digital orthodontics is designed to save you from all these issues. It saves time, reduces errors, and makes your patients smile more.
In this article, you will explore the benefits, applications, and core technologies behind digital orthodontics that enable you to work faster.

Why are Clinics and Labs Shifting to Digital Orthodontics?
It involves the process of using computers and smart tools to fix old and dead teeth. It is not like the old way with messy molds and guesswork. Dentists use scanners, 3D software, and machines to plan and make braces or aligners. It makes the dental job faster, cleaner, and more exact.
The end goal of digital orthodontic technology is to make treatment smooth for both the dentist and the patient. It reduces mistakes, saves time, and helps teeth move the right way. Digital orthodontics workflow is smart, simple, and the future of straightening teeth. These are the main reasons clinics and labs are shifting to digital orthodontics.
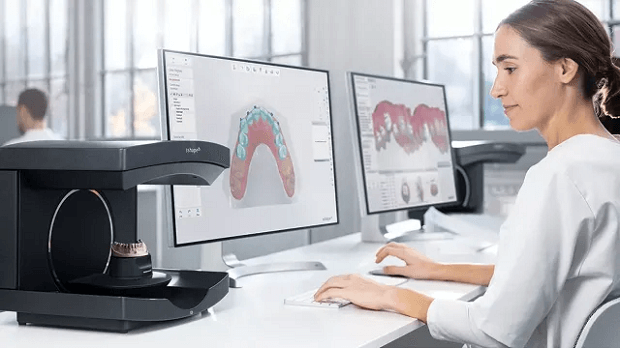
Types of Digital Orthodontic Solutions
There are three main types of digital systems used in digital orthodontics today. Each has its own process and is specific to the patient’s needs or requirements. Let’s take a look at the types of digital orthodontic treatment with key conditions.
– Clear Aligners
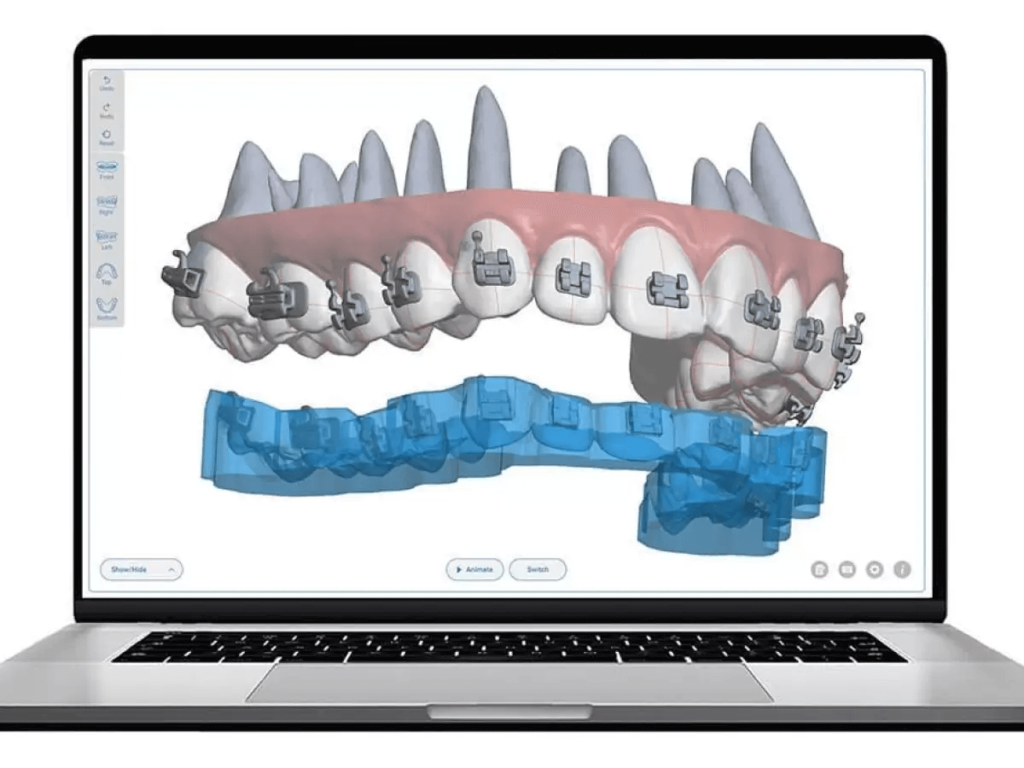
Clear aligners are thin, plastic trays designed specially for the movement of teeth. They are made after scanning the patient’s teeth with an intraoral scanner. The scan is changed into a digital 3D model. Then, software helps map out how the teeth will move with each aligner.
The patient wore each aligner for two weeks. Then, the patient moves to the next aligner. These trays are removable, so patients can eat and brush like normal.
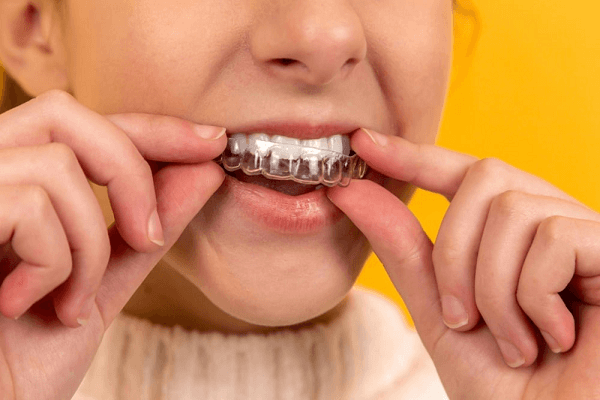

For dentists, aligners make treatment planning clear and visual. For lab technicians, the digital files are accurate and help in making aligners faster. This system improves communication between the clinic and the lab and cuts down on remakes or errors.
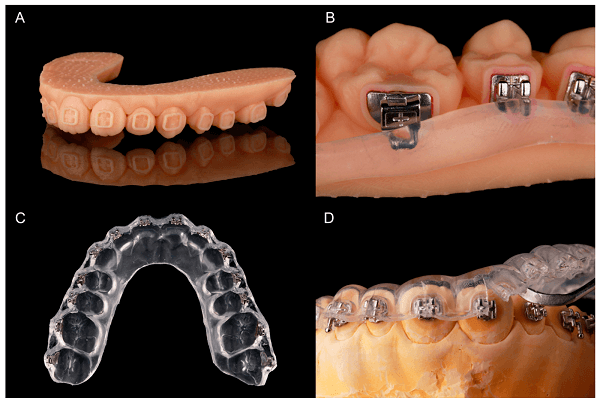
– Custom Digital Brackets and Wires
Digital orthodontics enables you to design bracket placement and archwire bends before even touching the patient. After scanning the mouth, special software changes your plan based on the final tooth position.
Once planned, a transfer tray is printed or made. This method is called indirect bonding. It saves time during bonding and improves accuracy.
Wires can also be customized using robotic wire-bending systems. These systems follow your plan exactly. For lab technicians, this method makes wire production more precise and keeps the orthodontist’s workflow smooth.
How Digital Orthodontics Works? Step-by-Step Breakdown
The working process of digital orthodontics involves certain steps. Each step enables you to make your job faster, cleaner, and more accurate. Here is a step-by-step guide that enables you to complete your dental digital orthodontics technology job without any manual errors.

– Digital Records and Scanning
The first step is to collect clear records of the patient. This starts with a 3D scan of the teeth. Instead of using a messy impression tray, the dentist uses an intraoral scanner. You can take fast and accurate pictures of the teeth, gums, and bite.
These pictures change into a 3D model. That model helps the dentist see the exact shape and size of each tooth. The dentist can save the scan as a digital file and share it instantly. The 3D imaging in orthodontics is also used later to compare progress.
– Virtual Setup and Treatment Planning
Once the scan is complete, the next step is to plan the treatment. You can use software tools to move the 3D teeth into new positions. The software can even show a preview of the patient’s final smile. That’s helpful for explaining treatment to patients and gaining their trust.
– Appliance Fabrication (Aligners or Brackets)
After you design the treatment plan, it’s time to make the appliance. This could be clear aligners or custom brackets and wires. Aligners are 3D printed or vacuum-formed using the digital model. Brackets are placed on a printed tray for accurate bonding.
Dentists share the files online with dental labs. That means less waiting for the patient and smoother work for the clinic. They also use tools to track the records of the number of trays or wires needed.
– Treatment Monitoring and Refinement
Once you complete your treatment, the next step is to monitor it. Dentists mostly scan the patient’s mouth during a visit. These scans are compared to the original plan to check if the teeth are moving correctly.
If not, changes can be made. These are called refinements. New aligners or wires can be made without starting from scratch. This step keeps treatment on track. It saves time, reduces errors, and improves the final results.
Core Technologies Behind Digital Orthodontics
There are strong tools behind the working process of digital orthodontics. These tools help you scan teeth, plan treatment, make appliances, and track progress. Let’s explore the key technologies that make digital orthodontics accurate and fast for dentists.
– Intraoral Scanning
In digital orthodontics, dentists mostly use an intraoral scanner. They use it to take clear pictures inside the mouth. It’s fast and doesn’t need any messy trays. The orthodontic digital scanners capture every tooth from every angle. This makes it easier to study tooth shape, position, and bite.
One good scanner many clinics use is the Aidite intraoral scanner. It’s small, simple to hold, and gives sharp detail. It captures full arches quickly and sends clean STL files to the lab. These files are easy for lab techs to open and use right away.
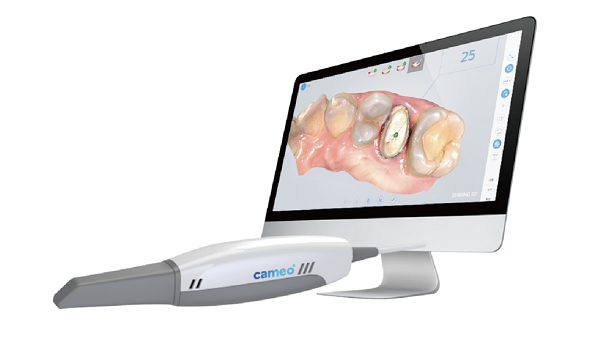
– Digital Treatment Planning Software
After scanning, the dentist uses software to plan how the teeth should move. This is called a digital setup. It shows each small change step by step. It also enables you to see the final smile before the first tray or wire is made.
Planning software enables you to fix spacing, crowding, and bite issues. It helps dentists choose the best method. The software also helps the lab know what to make and how many trays are needed.
– 3D Printer & Aligner Manufacturing
Dentists also use 3D printers in digital orthodontics to make accurate dental models. A 3D printer is used to print dental models. These models are used to shape aligners or make bonding trays.
The Aidite 3D printer is often used in dental labs. It prints fast, with high detail. It supports many dental resins. The printed models are strong and ready to use for forming aligners. The result is smooth and accurate. You can easily make crowns, bridges, and veneers without breaking the bank.

– Teledentistry in Orthodontic Monitoring
Digital orthodontics also uses tele-dentists to monitor the condition of crowns, veneers, and other restorations. Teledentistry enables patients to send photos or videos from home. This helps spot any slow changes or poor fits.
It also enables dentists to give feedback without needing a full in-person visit. If something needs to change, a new scan can be taken, and the lab can make updated trays fast. This can help avoid long gaps in care.
FAQs
What are digital braces?
Digital braces are regular braces made with digital tools. Dentists scan the teeth and plan the treatment on a computer. Digital braces help dentists save time and give better results for patients. They are clean, smart, and easy to manage.
What are the digital advances in orthodontics?
Digital advances in orthodontics include 3D scanning, digital treatment planning, clear aligners, and 3D printing. Dentists now scan teeth instead of using messy molds. They plan tooth movement on a computer.
What is the difference between Invisalign and orthodontics?
Orthodontics is the field of fixing crooked teeth and bite problems. Invisalign is one type of clear aligner used in orthodontics. It is made of smooth plastic and is nearly invisible. So, Invisalign is a tool used in orthodontics, not a separate thing.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, digital orthodontics makes treatment easier, faster, and more exact. It helps dentists plan better and helps labs make better tools. This system changes the way braces and aligners are done, from start to finish.
Digital tools work in many areas. You can use them for clear aligners, metal braces, or even mixed systems. Scanning, planning, and printing all happen in one flow. This means fewer errors, less mess, and more comfort for the patient.
To avail all these benefits, it’s important to choose the brand that provides a cost-effective digital orthodontics solution. A trusted name in this space is Aidite. Their scanner and printer make strong, clean models for labs. These tools work well together and fit into an everyday clinic.