3D printing has changed modern dentistry by replacing old methods with accurate, customizable solutions. 3D-printed dental models make it easier to diagnose problems, plan treatments, and explain procedures to patients. They also speed up production and cut costs. This assists with braces and surgical planning. It produces better outcomes and more satisfied patients. In this article, we will talk about the various types and how they are produced. We will also read about the materials, benefits, and costs of 3D-printed dental models and their role in dentistry.
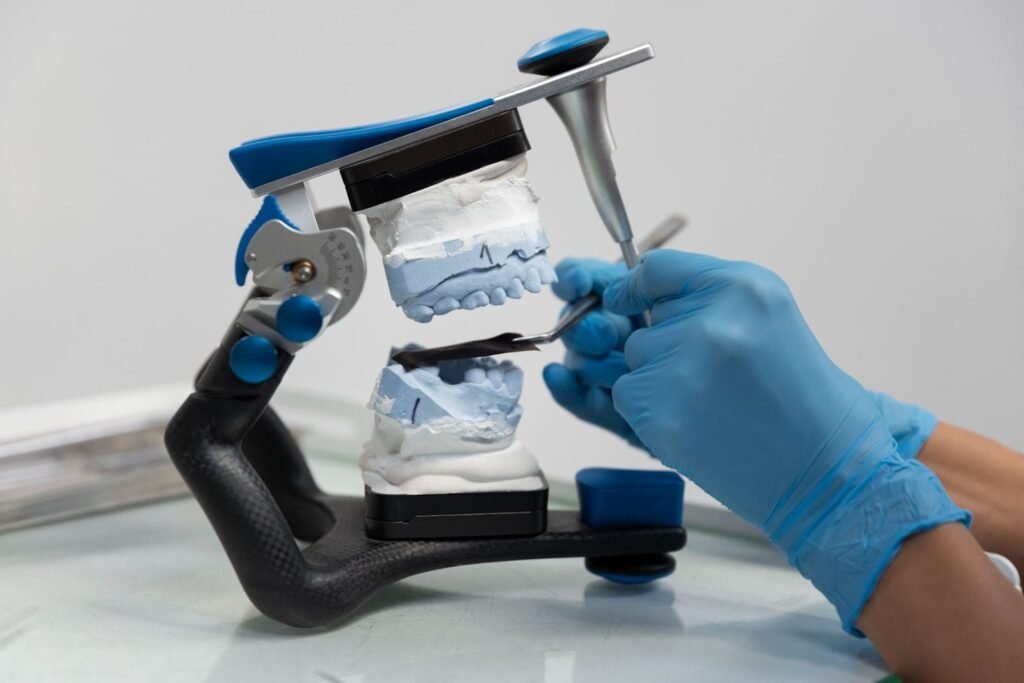

- What Are 3D Printed Dental Models?
- Different Varieties of 3D-Printed Dental Models
- The Process of 3D Printing Dental Models
- Materials Used for 3D Printed Dental Models
- Advantages of 3D Printed Dental Models
- Cost of 3D Printed Dental Models
- How to Choose the Right 3D Printing System for Dental Models
- FAQs
What Are 3D Printed Dental Models?
Modern 3D printing creates dental models that copy the exact shape of a patient’s teeth. 3D-printed dental models are replacing traditional plaster models because they are more accurate, provide personalized services, and allow faster work. These models are important for:
- Diagnosing dental issues
- Planning treatments
- Educating patients
Traditional methods are being replaced by digital scanning and CAD/CAM systems, improving workflow efficiency and eliminating measurement errors. 3D-printed dental models offer benefits such as cost-effectiveness, faster turnaround times, and versatility in orthodontics, surgical planning, and patient education, driving modern dental practices toward more efficient and precise care.
Different Varieties of 3D-Printed Dental Models
For dentists and learning, 3D-printed dental models are beneficial in many ways. Each provides different advantages that enhance the quality of dental work and patient service. There are a variety of 3D-printed dental models – when selecting the best one, it’s fundamental to take into consideration the different types.
1. Diagnostic Models:
Diagnostic models, which are extremely useful in a case assessment and treatment plan. These models help dentists identify issues while developing precise treatment strategies by representing detailed patient oral cavities.
2. Orthodontic Models
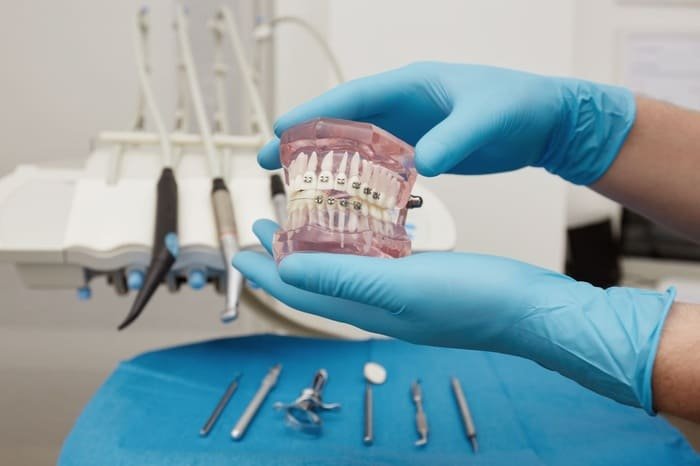
Orthodontic models function as essential tools for designing all appliances, including braces, retainers and aligners. Through accurate fitting and proper alignment, orthodontic models produce superior patient outcomes.
3. Surgical Guides
Dental Surgical Guide help dental professionals perform precise implant procedures, reducing surgery time and enhancing patient safety. For practices that frequently perform surgery, investing in 3D printing technology for bases for 3D-printed dental models is a cost-effective approach.
4. Crown and Bridge Models
The models produce dental restorations to create crowns and bridge fixtures. These models establish a direct relationship between their precision level restoration stability and patient comfort.
5. Educational Models
These models help explain treatment plans to patients and educate dental students. By using 3D-printed dental models, clinics can save on the cost of traditional materials and provide better learning tools.
3D printing technology shows its ability to adjust to various dental applications across modern dentistry through its diverse model types.
The Process of 3D Printing Dental Models

The process for producing bases for 3D printed dental models is streamlined through modern dental 3D printing technologies, which include:
Digital Scanning: Modern scanning technology provides patients with the comfort of digital processes, which deliver better impression output.
CAD Design: Dental specialists use a CAD software platform to obtain and support scanned data to develop the appropriate models. They are specifically designed and fine-tuned to fit each patient’s specific needs during the manufacturing process.
3D Printing: After a design process, the object is prepared for 3D printers. The final model is built from several materials via additive build processes. Some of the most common 3D printing technologies used in dentistry are:
- Stereolithography (SLA): Best for precision and detail.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Faster and equally precise as SLA.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Low-cost, ideal for educational prototypes.
After Printing: The printed model is kept to undergo specialized maintenance processes before it can reach the final stage used to undergo curing treatment. Post-print processes create precise clinical applications through model surface topography normalization, strength enhancement, and precision refinement.
Materials Used for 3D Printed Dental Models
Selecting appropriate materials for dental 3D printing plays an essential role in creating precise models that combine robustness with adaptable design requirements alongside their relevance to dental applications to achieve maximum quality outcomes.
- Resins: Dental Resin materials deliver exact production together with adaptable design capabilities to support diagnostic tools that benefit surgical interventions and dental restoration work.
- Plastics: Plastics remain affordable for educational and prototyping models, yet dental resins deliver flexibility when combined with stability and excellent performance in non-medical patient support applications
- Biocompatible Materials: Surgical guides with combined temporary restorations require materials which conform to essential safety parameters for patient health needs.
Essential characteristics of these materials are:
- Durable: It guarantees long-term use.
- Flexibility: Essential for orthodontic and surgical integration.
- Precision: It is critical that these materials fulfill the accuracy required during clinical applications.
Advantages of 3D Printed Dental Models
The use of 3D-printed dental models brings about evolution in workflow through increased efficiency along with better accuracy, cost-reduction, and patient satisfaction.
Accuracy and Precision
Healthcare professionals use their expert modelling skills to create precise representations which produce exceptional clinical outcomes despite digital workflow errors.
Speed and Efficiency
Through 3D printing, the production duration decreases far beyond that of standard manufacturing techniques. The more seamlessly the dental process gets carried out, the faster dentists and patients are served.
Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing technology reduces costs in dental procedures by minimizing waste and labour, offering long-term financial benefits despite the high initial equipment investment.
Customization and Versatility

Dental specialists leverage 3D printing technology to create custom-fit models that precede several stages of patient assessment and surgical execution.
Improved Patient Experience
As we improve the visualization of what treatment design even looks like for patients, paired with improved patient communication, we create better patient benefits.
3D printing technology delivers multiple advantages that show its power to transform dental operational efficiency and dental patient care.
Cost of 3D Printed Dental Models
Several factors influence the cost of 3D-printed dental models:
Equipment Costs:
3D Printer Types: The printer’s cost depends on its technology type.
- SLA (Stereolithography) Printers: Liquid crystal and light or stereolithography printers are used within dental model applications where precision requirements exist while their purchase cost varies from $3000 to $50000 based on the selected resolution capabilities.
- DLP (Digital Light Processing) Printers: These range from $2,500 to $40,000. With superior resolution capabilities, DLP printers outdo SLA printers to quickly create 3D dental model prototypes.
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) Printers: Industrial use applications find FDM printers cost-effective at $200 to $10,000, while these printers fail to meet requirements for dental model precision because of insufficient resolution potential.
Material Costs:
- Resin: You can get dental-grade resins for 3D printed dental models for about $50 per litre; specialized bio-compatible resins for surgical guides can go up to $150 per litre, depending on their durability, accuracy, and biocompatibility.
- Plastic Materials: Typical thermoplastics for societal FDM printers, like PLA and ABS, are priced at $25 to $100 per kilogram but are vastly inferior in precise dental applications compared to resins.
- Specialty Materials: Bio-compatible materials which serve dental surgical guides and models typically run between $200 to $300 per litre according to their specific formulation requirements.
Design Complexity:
- Simple Models: Creating a basic dental diagnostic 3D printed dental model requires $10-$50 materials and takes between 1-3 hours of print time.
- Complex Models: The creation of surgical guides and custom dental prostheses demands complex production protocols, leading to material costs between $50 and $200 while requiring production times extending from 4 to 12 hours or more.
Post-Processing Costs:
The production of new dental products demands careful post-printing tasks, which start with product cleaning followed by curing procedures and possible support structure elimination.
This can add additional costs:
- Cleaning and Curing: Model-based post-processing costs between $5 and $30 per piece according to both dimension and processing needs.
- Labour Costs: Services that include technician time for post-processing usually charge between $15 and $50 per hour.
Operational Costs:
- Energy Consumption: 3D printers require electricity yet operate at a low cost, which is estimated at $1 to $5 per hour based on their size and print duration.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance, software updates, and repairs can add $500 to $2,000 per year to operational costs.
The dental applications of 3D printing provide budget-friendly solutions that both diminish resource waste and raise the availability of care while providing enhanced treatment benefits.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printing System for Dental Models
Dental professionals should consider the following factors when selecting a 3D printing system:
- Printer Type and Technology: Ensure the printer meets the required precision for 3D-printed dental models.
- Material Compatibility: When choosing a printer dentists need to select one that can handle raw materials produced for dental applications.
- Cost and Maintenance: Consider the long-term cost of 3D-printed dental models, including material costs, printer maintenance, and labour.
- Technical Support and Training: Organizations require dependable support and training systems to gain a smooth reception into their standard work processes.
The evaluation process of multiple critical elements helps dental practices select appropriate equipment systems, producing high-quality results. The Aidite 3D Printers system provides dental professionals with durable, affordable and dependable models while retaining flexible features to achieve remarkable outcomes in dental operations.
FAQs
Is 3D printing technology leading to greener practices in the use of dental modelling when compared to traditional methods?
Indeed, 3D printing technology reduces the demand for stone and plaster in manufacturing operations, making it environmentally friendly.
How long does it take to build a dental model with 3D?
Building a 3D-printed dental model takes approximately one to two hours for a typical print duration. Model complexity, along with printer type, determines the total production duration.
Can 3D-printed dental models be reused?
Three-dimensional dental models printed for diagnostic operations function as one-time items because such devices serve unique treatment and assessment needs. For reference or educational needs, these models can be stored, but their primary use remains diagnostic.
Do 3D-printed dental models present safety conditions for primary mouth usage?
3D printed models receive intraoral use only when made from biocompatible materials which fulfill official requirements for surgical guides and temporary restoration applications. Regular diagnostic models function best when kept outside the mouth.
What level of precision do dental models achieve when produced by 3D printing when compared to conventional dental model creation?
3D-printed dental models function within a precision window of microns, which surpasses the standards of traditional model prototype accuracy. The model accuracy, which meets dental application requirements, depends on three key aspects: scanner type, printer selection, and raw material specifications.
Conclusion
Through the 3D printing of dental models, clinicians can achieve exact procedures at a faster speed and at a lower expense, thus improving both diagnosis and treatment along with patient care quality. The combination of improved digital workflows and Aidite 3D Printers helps healthcare organizations reduce waste and achieve reliable, high-quality outcomes. Future technological development will extend dental applications, which will promote innovative practices and produce better clinical outcomes.