For dental professionals who want to restore long-term, high-strength restorations, learning how to bond zirconia is an essential skill. The unique properties of zirconia require a thoughtful process when bonding it. Thus, with help from trusted dental innovators such as Aidite, clinicians can yield optimum results when employing the suitable materials and processes used specifically for zirconia. This guide outlines the essential zirconia bonding techniques and tools that will enable professionals to take their practice to the next level, including zirconia bonding failure prevention! From choosing your zirconia to refining your method, work through the zirconia bonding steps to master clinical success.
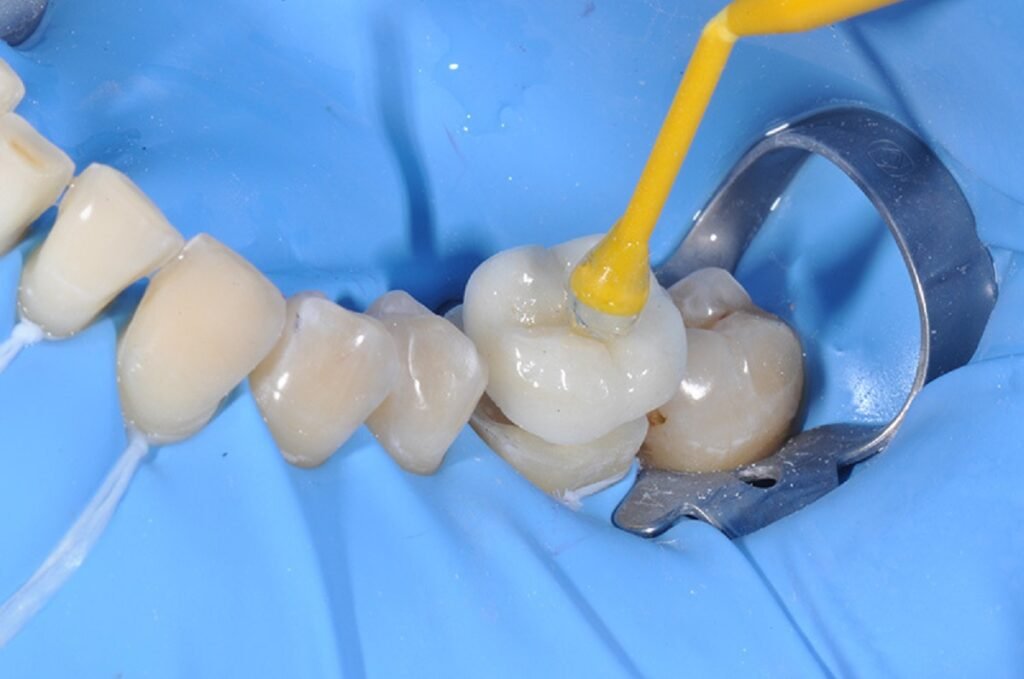
Understanding How to Bond Zirconia
To understand how to bond zirconia, it is first helpful to clarify what zirconia is. Aside from that, zirconia has no silica phase, unlike traditional ceramics; therefore, conventional etching and bonding techniques are ineffective. That means the use of specialized protocols to obtain a long-lasting adhesive bond.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Bond Zirconia
If you are to bond zirconia successfully, here are the zirconia bonding steps that you will need to follow.
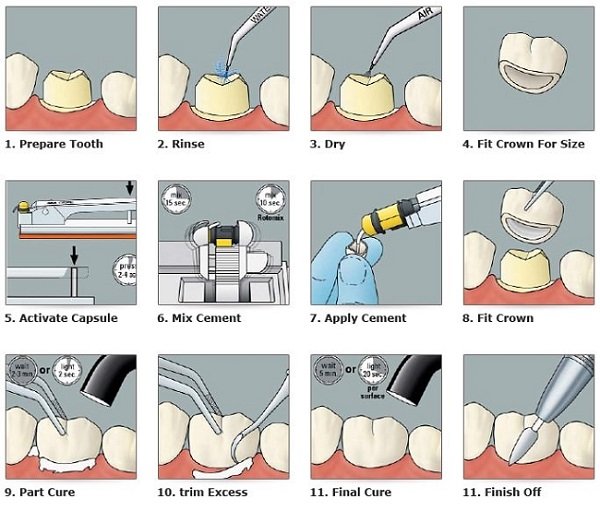
Step 1: Surface Preparation
Sandblast the inner aspect of the zirconia bonding surface treatment with 50-micron aluminum oxide at 1–2 bar pressure. The method treats the zirconia bonding surface to obtain micro-retentions by expanding the surface area to improve mechanical adherence. If sandblasting your work, be sure to use a clean, oil-free sandblaster and take care to never sandblast for too long to avoid destroying zirconia.
Step 2: Cleaning
Following air abrasion, the removal of contaminants such as saliva, oils, and polishing debris is critical. Either rinse with a zirconia-specific cleaner or through ultrasonic cleaning in 5–10 minutes with either alcohol or distilled water. Cleaning of zirconia restorations. Paralleling the natural bonding mechanisms, effective cleaning of zirconia restorations is essential in the prevention of zirconia bonding failure and prevention surface reactivity for bonding with primer.
Step 3: Primer Application
Apply a phosphate monomer containing primer, 10-MDP primers, and chemical zirconia bonding agents. Apply a thin, consistent layer onto the inner surface of the restoration, leave for the prescribed time (typically 60–180 seconds), then air-dry. Zirconia-based chemical. This chemical reaction is the first step in reliably teaching how to bond zirconia.
Step 4: Bonding Agent Application
This agent is applied with a high-performance zirconia bonding agent suitable for the selected primer. Dual-cure agents are favored as they give a reliable cure throughout the dentin, even in areas that are not light-exposed. Ensure even coverage and bond strength by applying a thin layer to both the tooth and the restoration surface.
Step 5: Zirconia cementation
Select a dual-cure resin cement indicated for zirconia bonding steps. Apply cement in the restoration, seat restoration over the prepared tooth, and hold firmly. Polymerize for 20–40 seconds on each surface after removing excess cement. Keep occlusion checked, and it should not be high after cure, which will interfere with retention.
Step 6: Light curing
Polymerization is initiated by seating the restoration, followed by light curing each surface of the restoration for 20-40 seconds. Avoid areas where microleakage or debonding may occur as a result of varying margins cured under and over these areas, as well as microleakage from the opposing occlusion.
Step 7: Marginal Finishing
After curing, carefully finish the margins and polish them, making sure that have no resin flash left. This makes it even more comfortable for the patient, keeping plaque away and keeping your restoration viable for as much time as possible.
Step 8: Post-operative Evaluation
Book a follow-up appointment for evaluation of occlusion, marginal integrity, and overall function. The early identification of these problems is beneficial for zirconia bonding failure prevention.
The above zirconia bonding steps constitute the foundation for a successful and predictable bonding protocol. Understanding how to bond zirconia affects surface treatment, cleaning, adhesive, and cementation use, giving clinicians the information necessary to achieve optimal clinical outcomes with minimal risk of failure.
The Role of Zirconia Bonding Agents
The use of quality zirconia bonding agents is critical in achieving successful bonding. The purpose of these agents is to improve the bond strength between the zirconia restoration and the tooth structure. Choosing a proper bonding agent for luting zirconia. One of the critical steps in learning how to bond zirconia.
The key points for zirconia bonding agents:
- Chemical composition: Bonding agents with 10-MDP create strong chemical bonds with zirconia and increase the longevity of adhesion.
- Curing Compatibility: Dual-cure bonding agents are well-suited for areas, that are inaccessible for light, ensuring a thorough polymerization.
- Ease of Application: Super-user-friendly agents help prevent operator error and allow clinicians to achieve a steady level of quality.
- Storage Stability: An extensive shelf life guarantees that the adhesive will be effective during its usage span.
- Clinical Validation: Selecting agents with established clinical study evidence provides more confidence in long-term success.
Zirconia Bonding Surface Treatment
Effective zirconia bonding surface treatment is vital. This usually includes air abrasion sandblasting with aluminum oxide, which roughens the surface and encourages mechanical interlocking. Also, the priming of these surfaces with a primer containing a phosphate monomer further helps to optimize bonding. Understanding how to bond zirconia requires mastery of this zirconia bonding surface treatment.
Key steps in zirconia bonding surface treatment include
- Air Abrasion: Use of sandblasting before treatment to roughen the surface through 50-micron aluminum oxide, which aids in enhancing the topography for micromechanical retention.
- Cleaning Protocol: Clean using ultrasonic or exclusive zirconia cleaners to prevent hard surface debris from bonding and causing contamination.
- Primer Application: Apply a primer with 10-MDP monomer to create a strong chemical bond with the zirconia.
- Moisture Control: Keep the surface tidy and dry before the bonding activity to prevent the bond from being weakened.
- Avoid Silane: Silane is not effective on zirconia, use zirconia-specific primers only.
Common Pitfalls and Zirconia Bonding Failure Prevention
The cause of failures is often improper surface pretreatment, mixing, or using incompatible bonding agents. Knowledge for zirconia bond failure prevention encompasses:
- Inadequate Surface Roughening: Omission or inadequate sandblasting will reduce micromechanical retention and ultimately weaken the bond.
- Contamination: If saliva or any kind of oil is on the zirconia surface, it may hinder bonding; be sure to clean the zirconia thoroughly before proceeding.
- Incorrect Primer Usage: Using primers with zirconia, such as silane, results in low chemical adhesion.
- Moisture Presence: Remaining moisture upon the restoration makes it hard for the bonding agents to adhere.
- Bonding Agent Incompatibility: Not all bonding agents work well on zirconia; always use compatible bonding agents.
These tips are important for anyone interested in learning about bonding zirconia.
Aidite’s Contribution to Effective Bonding
In addition to providing the best zirconia materials globally, Aidite provides education and tools to help clinicians as well. Their biomic connect is a leader in bond strength to lithium disilicate and zirconia. Click here to learn more about bond zirconia.
Aidite products aim to make the way to bond zirconia as easy as it can be, ensuring the bond strength and the aesthetics. Their solutions are based on the most recent academic and clinical guidelines.

Main Aidite Contributions to Zirconia Bonding
- Material Innovation: Aidite offers high-quality zirconia blocks for both excellent translucency and strength to deliver superior restorations.
- Bonding System Compatibility: Their products are made to be used with current bonding agents for zirconia with guaranteed longevity.
- Clinical education: Provide ongoing resources and technical support to professionals mastering how to bond zirconia.
- Research-Driven Solutions: All the products by Aidite are scientifically researched and clinically validated.
- Global Trust: Aidite technology and expertise are relied upon by dentists around the world in achieving successful zirconia bonding results with a consistent and proven track record around the globe.
FAQs
Q1. What is unique about zirconia bonding as compared to the bonding that occurs when working with traditional ceramics?
The absence of a silica phase in zirconia also means that the conventional etching is ineffective. It needs mechanical surface treatment and primers based on phosphate monomer to obtain effective bonding.
Q2. Why is using a zirconia-specific bonding agent important?
Zirconia is notoriously difficult for general bonding agents. In contrast, zirconia-specific agents include functional monomers such as 10-MDP that chemically bond to zirconia, providing more effective and long-lasting protection against debonding.
Q3. Can I use regular cement for bonding zirconia restorations?
No, standard cement does not have the required chemical affinity. In the case of zirconia, a special type of resin cement containing compatible primers and zirconia bonding agents must be used for an effective zirconia bonding capability.
Summary
So, how to bond zirconia choices and selection of materials, the right disinfectant type for zirconia bonding, proper zirconia bonding surface treatment, and successful zirconia bonding method steps. More importantly, mistake avoidance is the prophylaxis of zirconia bonding failure. Dentists and clinics now have access to innovative products and knowledge with Aidite as a new partner. Their dedication to quality still sets the course for the future of zirconia bonds. Aidite helps you improve your skills or learn how to bond zirconia to solve complex cases.