The practice of restorative dentistry involves a lot of accuracy, dexterity, and appropriate instruments to yield the best results. Every instrument used in the dental practice starting from cavity preparation to creating perfect restorations is important in delivering quality and effective dental treatments.
This guide offers the ultimate restorative instruments list, explaining where they are used and how they help to facilitate treatment. Regardless of the level of experience in dental practice, it is important to understand these tools to be well prepared to perform restorative procedures accurately.
Why Is Selecting the Right Restorative Dental Instruments Essential?
There are a lot of perks to selecting tools from a comprehensive restorative instruments list. First of all, Using the correct tools provides accuracy in any dental procedure, like fillings and dental implants. The quality restorative instruments in dentistry enable dental professionals or practitioners to work with greater control or precision and reduce the chance of mistakes that could lead to oral infection.
Furthermore, the right instruments improve efficiency. High-quality and well-designed tools enable dentists to complete the procedure with great speed and allow more time to look after the patient. This leads to increased productivity and minimizes patient discomfort. Furthermore, the quality instruments used in restorative dentistry also promote better infection control and present the cross-contamination of infection.
Types of Restorative Instruments and Their Uses
Understanding the different types of restorative instruments in dentistry contributes significantly to the success of dental procedures and the overall patient experience. Here are the detailed overviews of the restorative instruments list and their uses.
1. Diagnostic Instruments
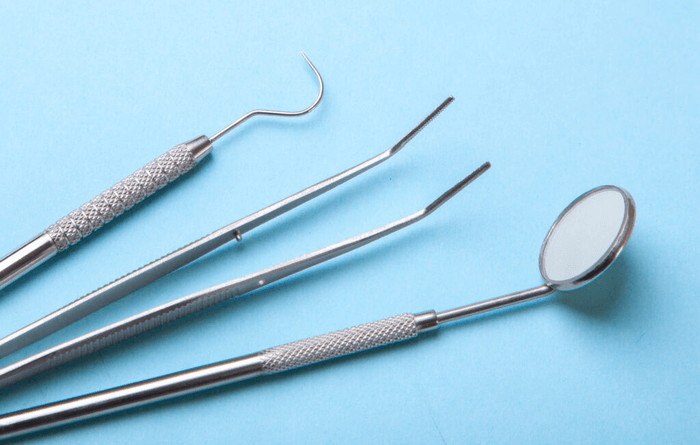
As the name suggests, these restorative instruments are used to assess the patient’s teeth and gum condition before starting any treatment or procedure. Common tools in this instrumental category include mouth mirrors, explorers, and periodontal probes.
- Mouth mirror: This tool is useful when inspecting areas of the mouth that are difficult to view without the help of a mirror such as the rear of a molar or the floor of the tongue. It also enables dentists to direct light on the dark surfaces, making it easier to see during examination. Additionally, the mirror allows the pulling of cheeks and tongue backward, which provides a good view of the teeth and gums.
- Explorer (Probe): An explorer is a sharp-ended instrument that is used to feel for cavities, fractures, or any other uneven surfaces in the teeth or gum. It is commonly known as the dentist’s third eye. It is valuable for detecting first signs of caries and assessing the surface of restorations to maintain dental health.
- Periodontal probe: This restorative instrument is used to determine the depth of pockets that surround teeth to determine the general health of gums. The periodontal probe is an essential tool in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases, especially deep pockets or gum recession, and helps in preventing gum-related diseases in the future.
2. Tooth Preparation Instruments
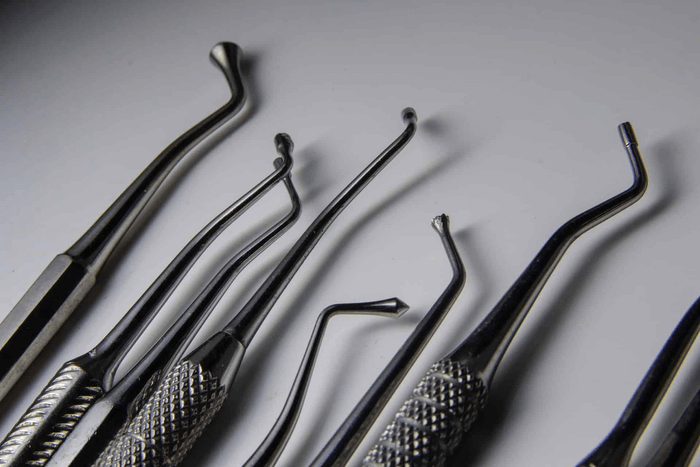

Dentists rely on a variety of tools from the restorative instruments list to shape and prepare the tooth for restorative procedures such as fillings and crowns. The key tools in this category are excavators, chisels, and hatchets.
- Excavators: Excavators are mainly used to remove the decayed tissue from the tooth and to avoid further decay. They are also involved in the carving of the tooth surface to improve the adhesion between the tooth and the restoration material. Excavators are very careful in the removal of soft or decaying dentin so that only the affected area of the tooth is removed and the least amount of healthy tooth structure is taken.
- Chisels: This restorative instrument in dentistry is used in shaping the enamel walls during the preparation of cavities for a filling. They are especially effective in eliminating small particles of unsupported enamel or in establishing precise, neat margins for restoration. The chisels used in carving provide a close tolerance for fillings or crowns, thereby increasing the longevity and beauty of the restoration.
- Hatchets: Hatchets are small, rotary instruments used to cut and shape teeth to get the best fit for the restoration. Due to their ability to remove hard materials such as enamel or dentin with a high level of accuracy, they are very useful in preparation procedures.
3. Restorative Instruments
This type of instrument, often highlighted in a restorative instruments list, is designed for a dentist for placing and contouring dental material to restore teeth to their natural function and appearance.
Common tools include amalgam carriers, composite placement instruments or condensers, and burnishers or carvers.
- Amalgam Carrier: Amalgam carriers are used to transport and place filling materials into cavities. They simplify the process and enable it to be done in the quickest time possible to ensure the material is applied appropriately with less wastage.
- Composite Placement Instrument: These instruments are used to contour and adapt composite materials when they are at rest during restoration procedures. They assist the dentists in providing a smooth and even plane that would give a natural appearance as well as durability.
- Burnishers: Burnishers are utilized to polish restorative materials, and make restorative work look more natural and blend with the natural teeth. They also decrease roughness in order to minimize plaque formation.
4. Rotary Instruments
Rotary instruments are super-powered hand instruments in dentistry that are used for a variety of oral procedures, including cutting, grinding, and polishing teeth.
Handpieces and burs are common rotary instruments. Dentists use handpieces to remove decay tissues, smooth out cavities, and prorate the patient teeth for fillings. While the burs come in various shapes and sizes for specific tasks. The primary benefits of rotary instruments include reduced time and improved procedure precision.
5. Polishing Instruments
Polishing instruments are used to smooth and shine the teeth’ surface and make restorations that enhance teeth’s aesthetics and reduce plaque accumulation. The restorative instruments named under this category are polishing brushes, rubber cups, and polishing discs.
- Polishing Brushes and Rubber Cups: These restorative instruments in dentistry are used to polish restorative dental material with the aid of polishing paste to give a smooth and shiny surface. These tools are most useful when the surface of the restoration such as a composite filling or crown has become contaminated with stains, micro-scratches, or other blemishes.
- Polishing Discs: Polishing discs are utilized to refine and finalize the surface of fillings or crowns to blend with the natural teeth. These discs come in different grits; this enables the dentist to perform both rough and fine polishing depending on the situation. Polishing with discs improves the look of the restoration, giving it a more normal luster and guarantees the patient’s comfort since a rough surface can cause discomfort to the tongue or cheeks.
6. Accessory Instruments
Accessory instruments are supportive tools that assist in dental procedures, but they don’t directly impact the restoration itself. The dental restorative instruments named under this category are forceps, hemostats, and spatulas.
Forceps are used to hold or remove the small parts of dental materials and are commonly found in a restorative instruments list. While dentists use hemostats to control bleeding by clamping blood vessels. Spatulas help the dentist mix materials like dental cement and impression material. They enhance the density ability to manage materials and tissues effectively.
7. Specialty Instruments
Specialty instruments are designed for specific procedures. The list of restorative dental instruments includes periodontal scalers, surgical scissors, and implant placement kits.
These instruments are used to remove the plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line. The surgical scissors are designed to cut soft tissues, while implant kits are used for placing implants precisely.
What Factors Should You Consider When Selecting Restorative Instruments?
- Instrument quality and durability: Quality is key. Before reviewing the restorative instruments list, make sure it is made of high-quality materials like stainless steel or titanium. Both these materials provide durability and minimize the risk of infection for patients during treatment.
- Compatibility with existing equipment or tools: The compatibility of instruments used in restorative dentistry with other or existing dental equipment is also considered before making a final decision.
- Cost-effectiveness: Budget is also a key factor that impacts the investment. It’s important to focus on quality but make your budget balance according to the quality and features of tools.
- Ergonomic design: The ergonomic design of the instrument is essential for dentist comfort. Make sure to select restorative instruments that have ergonomic handles to reduce hand fatigue. All the same, the instruction should be well-designed to provide greater control for better treatment outcomes.
FAQs about Restorative Instruments List
1. Which type of instruments are utilized most in restorative dentistry?
The most frequently used instruments in restorative dentistry include dental handpieces, composite placement instruments, amalgam carriers, and other essential tools like burnishers and dental mirrors. Each is important in attaining accurate results as stated in the following sections.
2. Which instrument is used in amalgam restoration?
Special tools needed for amalgam restoration include amalgam carriers for carrying the material, condensers or pluggers for packing amalgam into the cavity and burnishers to polish the surface of the restoration. These tools make sure that the restoration is permanent and blends well with the rest of the patient’s teeth.
3. How are restorative instruments cleaned and disinfected?
Restorative instruments are cleaned and disinfected by autoclaves, which are high-pressure steam that kills bacteria and viruses. Following sterilization, instruments should be left to dry, checked for signs of wear and damage and put away appropriately to retain their efficacy and to avoid compromising the health of patients in subsequent operations.
Conclusion
To sum up, having a comprehensive restorative instruments list and selecting high-quality instruments is important for achieving precise, efficient, and successful dental treatment. Before choosing the right dental restorative instruments, key factors like quality, durability, compatibility, and customer support should be considered. All these factors help dentists choose the right tool for dental procedures.
Aidite is a standout brand that meets all these factors and provides high-quality dental instruments with excellent customer support. The tools of this brand can greatly enhance both clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction.